by Raj Pandya, Annual Meeting Co-Chair
The theme of this year’s annual meeting is communication, and I think one of the hardest parts of communication is listening. I find it embarrassingly easy to slip into broadcast mode, and imagine that simply because I want to say it, others will be interested. My 8-year old daughter can be brutal about this: “Daddy, this is boring, can we talk about horses, please.” (I will say, though, I can sneak in a little thunderstorm talk if we frame it around storms’ impact on horse happiness).
So, I am especially looking forward to this annual meeting as a chance to listen, especially to communities we haven’t interacted with before or in places we haven’t gone. There are lots of opportunities in this meeting. The presidential forum opens the meeting with some suggestions about how to address what audiences may be interested in and how to present information in a way that connects. There is a themed joint session on Thursday called “Ways of Knowing” that will explore things from an indigenous perspective. Sunday night, before the meeting kicks off, students will be presenting their research – a great chance to listen to the next generation. On Tuesday, a panel will tackle the challenge of communicating – and listening –across our various disciplines and another set of talks will focus on communication and diversity. Finally, there are sessions that explore communication from a user perspective – including public health, energy, and people interested in tropical cyclones.
The second hardest part about communicating is adapting. I find myself clinging to my preferred mode of communication, even when the audience and circumstance change. It doesn’t always work – in the words of Hawkeye Pierce, “He doesn’t understand loud English, either, Frank”. Even only in English, there are new social media and devices that are rapidly changing the way we communicate.
There are a number of talks at the Annual that tackle this. There are sessions on mobile devices and e-books and a more general session to explore technology that enables communication. There are special sessions demonstrating technology in education and a special session on Thursday looks at how data publishing may change the way we communicate science.
Yogi Berra is reported to have said a whole lot of things, including “You can observe a lot just by watching.” In the spirit of this year’s Annual Meeting, with the theme of communication, I’d suggest, instead: “You can hear a lot by just listening.”
Have fun.
weather communications
NWS sez 'Hi' to Fort Worth on Facebook
The National Weather Service is on Facebook (so is AMS, actually). But you knew that already. What’s new is that now the NWS is trying out Facebook as a local-level communications tool. The Fort Worth, Texas, office has a new page to raise weather awareness locally. If weather turns ugly, it might become an important additional channel between meteorologists and the public.
Writes one commenter, “About time you guys got on here.” But actually, social media and government weather services have had a somewhat tempestuous relationship so far, even with the undeniable popularity of the national NWS fan page.
At least one NWS employee already had tested the waters on his own: in an April 30 severe weather outbreak one local forecaster in Arkansas was posting weather updates on a private Twitter account, minutes before the same information made it to TV screens. In response the Weather Service reiterated its policy against employees using unofficial communication channels for official business, effectively prohibiting social media for local weather communications.
More recently, the head of forecasting at Taiwan’s Central Weather Bureau, Ming-Dean Chen, used his personal Facebook page to distribute typhoon information hours in advance of the official notices from his own office. He expounded on possibilities that weren’t discussed in the official forecasts. Chen ended up apologizing to superiors, but pointed out that he was merely repeating information that had already been posted on the Japan Meteorological Agency web site anyway.
Renegade incidents seem less likely now that NWS is cautiously dipping an official toe in Facebook waters for local purposes. They could start a tidal wave, however, if they don’t proceed judiciously. Digital Meteorologist blog points out that a strong social media presence by local NWS offices might rapidly erode the long-held niche broadcast meteorologists have enjoyed by combining local weather knowledge with direct access to the public.
Sure, the US government is slow, but what happens when it finally catches up? #NWS could be a pretty powerful hashtag….Poke the bear if you want. Just make sure you are ready to run when he wakes up.
The Toughest Part of Forecasting
The New Zealand MetService’s chief forecaster Peter Kreft writes:
Getting the message out about severe weather, particularly when it involves rapid changes, requires excellent communication with the New Zealand public and many organisations managing weather-related risks. The message needs to be relevant and clear – not always an easy task, given that users of weather information have such diverse needs….In some ways, the challenge of getting the communication right is even more difficult than getting the meteorology right.
After recent events in New Zealand, Kreft should know. For days, the MetService had been tracking developing conditions for severe weather for parts of New Zealand. Then, on Wednesday, September 15, forecasters actually issued an advisory for gale force winds and “bitterly cold” weather several days ahead.
That’s when the other part of forecasting–the tough part- started to go awry. The media made references to a “massive” storm the size of Australia about to go medieval on New Zealand. References to civil defense authorities making preparations for the worst also hyped up the alarm.
[S]hortly after the MetService press release on Wednesday, this communication process was thrown off kilter by a media article about “the largest storm on the planet”. The article was based in part on the MetService press release but included information from other sources as well as a measure of journalistic licence.
Not surprisingly, weather discussion boards, blogs, and more media went haywire. Kreft says the misconstrued warnings went “viral”:
Within a matter of hours, MetService was fielding calls from people concerned about the “massive storm heading for New Zealand” and asking for clarification on various statements that MetService had apparently made. It was clear early on that people were confused about the source of the information they were receiving, and had been misled into thinking that the whole country was in for serious weather.
Not only worried citizens and nervous farmers but even disaster-preparedness authorities got caught in the storm of “mediarology.”
Unfortunately, MetService’s ability to get weather information to those who really needed to know was significantly hampered by media articles over-stating the area affected by the storm.
While severe conditions indeed occurred, the weather, as meteorologists had expected, was not bad everywhere in New Zealand
…leaving many people wondering what all the fuss was about. The danger this raises is that some of those may simply ignore the next Severe Weather Warning they receive.
All in all, it was a good reminder for why the weather enterprise continually needs to foster the partnership between scientists and the media, and ultimately the communication between forecasters and the public.
Not Seasick…Science Smitten
What if you are asked to be part of a scientific expedition aboard a non-luxurious research vessel, surrounded by complete strangers, forced to face rough seas – and sea sickness, 16 hours’ work shifts, no weekends or recreational activities, no days off, lots of hours under the sun working with scientific equipment, poor internet connectivity and no interaction whatsoever with the outer world? While many people would say: “no thank you”, I was euphoric when I received an email which first line read: “Congratulations, you have been selected as a participant of the Sixth Aerosols and Oceans Science Expedition”.
So begins Mayra Oyola’s engaging story of work aboard the NOAA research vessel Ronald H. Brown for the AEROSE campaign

under the auspices of Howard University, NOAA, and other institutions. It was apparently a love affair not just with the science and the sea, but with a lidar, too:
[E]very scientist is …assigned at least one particular instrument and is expected to become the one and only expert on that matter. In a sense, every scientist establishes a sort of “bond” with his/her assigned instrument that is very similar romantic affair. You can grow such a strong love and hate relationship with it. There are days when you two can get along just fine. But other days you have to fight against temptations (like throwing it overboard or smashing it with a sledge hammer). There are days when your appointed instrument gets seduced by Murphy (in other words, goes haywire) and you have to make him/her understand that s/he is in a monogamous relationship with you. As some partners, these instruments can be gold diggers (they cost hundreds/thousands of dollars) and are high maintenance as well.
And, this enticing view of the ocean:
When people say I must be crazy to have loved so much sailing on this expedition, I just ask them a couple of questions: Have you seen bioluminescence or done some fishing in the middle of the Atlantic basin? Or have you ever had the chance to catch a movie under the stars in the middle of the Sea? Well, I had. There are some great perks about sailing on the Brown. There is nothing as beautiful as lying on deck at night for the most spectacular stargazing sessions you will experience in this world. There are unusual things that you will never see in your everyday life: like watching a double rainbow or the most impressive towering cumulonimbus cloud EVER at the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITZC). I also loved watching different marine life forms like the flying fishes, dolphins and squids (oh yeah, we saw squids!). Oh and the sunsets… sunsets that will take your breath away!….But the highest reward is this: we get to do REAL science to solve REAL problems, such as improving the quality of satellite operations, understanding the effects of aerosols in hurricane formation and intensification and learning how tropospheric ozone can be linked to global warming, among many other things. There is nothing that can top that!
Check out the full story, and picture gallery, here, and kudos to Oyola for such drawing a compelling portrait of science at sea. We talk about the need to communicate science, and we’ll talk more about it as the Annual Meeting approaches, but she’s set a strong example already.
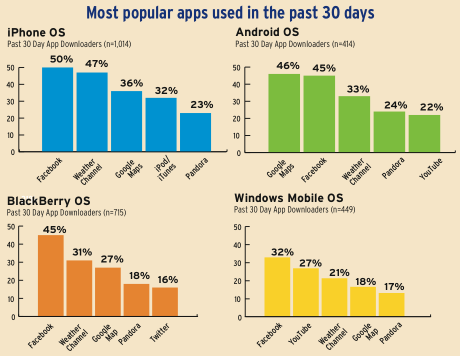
"Media" Is Short for "Meteorology"
Studies of local TV news have been telling us this story for years: weather is what drives people to the media. Now, Nielsen Co. is saying the same thing about smart phone applications use. Weather app downloads rank near the top for all platforms.
Here’s a chart from their study, announced today at the AppNation conference in San Francisco, as reported by SDTimes.