If you haven’t gotten your fill of science at the meeting, there’s more at the Fernbank Museum of Natural History. The museum strives to inspire life-long learning of natural history through dynamic programming and interactive science displays.

Along with their permanent exhibits, this month features a special exhibit, “My Favorite Things.” For the exhibit, each department chose a natural history piece from storage to put on display. The exhibit by nature is designed to appeal to scientists of all ages and fields in its diversity.
Of special interest to oceanographers, “Wild Ocean” is playing at the IMAX theater. Filmed on South Africa’s wild coast, the movie touches on the balance not only between the oceans and people but the relationship between all living things. Showing through March 11, show times are Monday through Saturday 11:00, 1:00, 3:00, and 5:00, with a 9:15 p.m. showing on Friday; and Sunday 1:00, 3:00, and 5:00.
We would tell you about the 7 p.m. extra showing this Friday (shhh!), but instead that’s when Richard Somerville author of the AMS-published book, The Forgiving Air, will give a talk on climate change at the museum.
Looking for Snow in Atlanta?
Northeasterners and those from colder climates visiting Atlanta may be trying to escape the snow during the Annual Meeting. But for those who aren’t, there’s a place nearby to play. Stone Mountain Park’s Snow Mountain, Atlanta’s first snow park, is a virtual winter wonderland.
The park includes a tubing hill and a 30,000 square foot play area, filled with a blizzard of snow activities. Although the manufactured snow is icy compared to the fluff that occasionally falls in Atlanta, the warmer air temperatures allow for more comfortable outdoor play.
Originally planned to open in 2007, the park was widely criticized for its plans to use one million gallons of tap water during a drought. The plan was changed to use water from the park’s own lake and the park opened last year.
Schedule Change
Unfortunately, due to a last-minute schedule change, David Schultz, author of the new AMS publication, Eloquent Science, will be unable to attend the Annual Meeting and participate in a number of presentations. However, Fred Carr of the University of Oklahoma graciously stepped in to cover the the “how-to’s” of publishing for David at today’s Student Conference, and the AMS book launch will still be held Monday (5:30-7:30 p.m.) at the AMS Resource Center (Exhibit Hall B2), at which AMS will be celebrating the release of three books–The AMS Weather Book, Eloquent Science, and Adaptive Governance and Climate Change (which will be released that day).
December East Coast Snowstorm a Cat. 3
Memories of the pre-Christmas snowstorm that paralyzed travel across megalopolis in mid December might not be as fresh as the severe cold snap that kicked off the new year east of the Rockies. But the storm, which dumped 1-2 feet of snow on the Mid-Atlantic, earned a Category 3 ranking on the Northeast Snowstorm Impact Scale, known as NESIS, classifying it as a “major” winter storm.
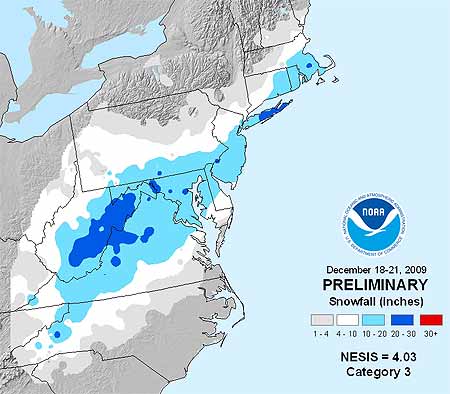
NOAA’s NESIS ranks Northeast snowstorms on a five-tier scale ranging from Category 1 “Notable” to Category 5 “Extreme.” It characterizes the storms based on how much snow falls (must deposit at least 10 inches); the size of the area affected, and the population of the impacted area. Developed in 2004 by renowned winter weather experts Louis Uccelini and Paul Kocin, both with the National Centers for Environmental Prediction, catalogs snowstorms dating back to 1888.
“Last month’s storm was one of only five in the past decade that ranked Category 3 or higher,” says Kocin. The others: December, 2002 (Category 3); February, 2003 (Category 4); January, 2005 (Category 4); February, 2006 (Category 3), and February, 2007 (Category 3). Topping the NESIS scale—and the only winter storms rated Category 5—are the “Superstorm” on March, 1993 and the “Blizzard of ’96” in January, 1996. Last month’s snowstorm fell short of the higher NESIS rankings for several reasons, explains Uccelini.
“While snowfall from the December storm ranked in the top ten for Washington, Baltimore and Philadelphia, the storm only provided a glancing blow to the New York City and Boston metropolitan areas and overall affected a relatively small area. This led to it being classified as a Category 3,” he says.
Although NESIS is the only snowfall index being used operationally by NOAA, there are NESIS-like indices being developed for other parts of the nation. At the AMS Annual Meeting in Atlanta, a presentation by Michael F. Squires (Wednesday, 20 January, 2:00 PM, B211) will discuss the Development of regional snowfall indices.
Addtionally, David Robinson of Rutgers University will introduce a new climate data record of satellite-derived snow cover extent in his presentation Northern Hemisphere snow cover extent during the satellite era (Wednesday, 20 January, 10:30 AM, B218).
Georgia’s Got a Groundhog, Too
He may not be Punxsutawney Phil, but General Beau Lee is the groundhog to look to for the winter forecast in Georgia. Although he doesn’t make his official appearance until February, Beau’s home, the “Weathering Heights” mansion at Yellow River Game Ranch (www.yellowrivergameranch.com), is a good getaway destination this week if you’re looking for meteorological curiosities or trying to entertain the family.
Located just two and one-half miles east of Stone Mountain on Highway 78, the ranch offers an opportunity not only to meet furry weathercasters, but other animals on an up close and personal basis. Walk down a mile-long trail on 24 wooded acres, where over six hundred birds and animals indigenous to the state of Georgia reside.
Located on the banks of the Yellow River, the ranch was affected by the heavy rains and floods in September, but fortunately no animals, nor the mansion, were in danger and the ranch is back to functioning as usual.
The Yellow River Game Ranch is open from 10:00 to 5:00 Monday through Friday and 10:00 to 6:00 Saturday and Sunday. For more details visit the Web site.
Light Show over Norway

An unusual atmospheric phenomenon over Norway (above, photographed by Jan Petter Jørgensen) and elsewhere in northern Europe recently led some people to believe they were witnessing alien activity. Only later did the Russian Defense Ministry reveal that a test of an intercontinental missile launched from a submarine in the White Sea had failed at the same time as the mysterious display in the sky appeared.
While the Russians didn’t directly connect the two, many military experts noted that a malfunctioning missile could give such a spiraling appearance. So while the Land of the Midnight Sun apparently isn’t also the Land of the Midnight UFO, it does bring up the question for you, our readers: How does a missile cause this spiralling effect? Here’s one possible explanation:
The Ballots Are In…Now Meet the Winners
With the New Year comes the season for annual awards and “Best of” lists of every kind, from Oscars to best beer to best iPhone apps. But how often do you actually get invited to the awards ceremony? Here in Atlanta you can practically walk the red carpet with the winners.
On Wednesday at 4:45 p.m. (Publisher’s Row, Exhibit Hall), Atmospheric Science Librarians International (ASLI) will be presenting its fifth annual ASLI Choice awards for the Best Books of 2009.
This year’s winner in the “science” category is Clouds in the Perturbed Climate System: Their Relationship to Energy Balance, Atmospheric Dynamics, and Precipitation, edited by Jost Heintzenberg and Robert J. Charlson. According to ASLI, it was selected for its “quality, authoritativeness, and comprehensive coverage of new and important aspects of cloud research.” 
A new category for “popular” books was added to this year’s awards, and the winner is this class is Planet Ice: A Climate for Change, with photography by James Martin and essays by Yvon Chouinard. It was chosen for “beautiful photography accompanied by thoughtful essays on a topical and timely subject.”
Runners-up in the “science” category are Aerosol Pollution Impact on Precipitation : A Scientific Review, edited by Zev Levin and William R. Cotton, for an “authoritative, well organized, forum-based approach to the evaluation of a problem of global significance”; Hydroclimatology: Perspectives and Applications, by Marlyn L. Shelton, for a “well-considered, well-referenced text on an important topic”; and Climate Change and Biodiversity: Implications for Monitoring Science and Adaptive Planning, by D. C. MacIver, M. B. Karsh and N. Comer, for “good, clear authoritative statistical compilations, graphics, and charts on a important subject.”

And if we may blow our own horn for a moment, the runner-up in the “popular” category is Jack Williams’s AMS Weather Book: The Ultimate Guide to America’s Weather, with ASLI noting “its accessible and informative approach to all aspects of weather, and the richness of its illustrations.”
Publisher’s Row will also be the place to find the AMS books booth as well as some of the other leading publishers of atmospheric science books. In fact, along with the AMS Weather Book, two of the other ASLI’s Choice winners are published by companies that will be displaying their titles at the meeting: Aerosol Pollution Impact on Precipitation (published by Springer) and Hydroclimatology (published by Cambridge University Press).
Congratulations to all the winners!
Dress for the Ocean's Success

A group of organizations supporting the creation of a national policy to protect oceans, coasts, and lakes has declared Wednesday, January 13, “Wear Blue for Oceans” Day. Rallies will be held in 10 cities across the nation, including San Francisco, New Orleans, Honolulu, and Washington D.C. To show your support, organizers are asking you to wear blue, even if you’re not attending, so here are two of our suggestions for tomorrow’s attire.

A Minimum of Maximum Concern
There are a lot of questions about the current solar minimum, which has reached historic levels—“No solar physicist alive today has experienced a minimum this deep or this long,’’ according to NASA’s Madhulika Guhathakurta, lead program scientist for NASA’s Living With A Star program, which studies solar variability and its effects on Earth. Some of the effects of the minimum are fairly clear to scientists: the amount of cosmic rays entering our portion of the solar system is greater than normal, and Earth’s ionosphere has shrunk.

The debate is instead partly about the effect of the minimum on Earth’s climate. A recent study by Judith Lean of the Naval Research Lab and David Rind of NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies suggests that decreased solar irradiance during the current minimum cycle may be slightly offsetting recent warming attributed to greenhouse gases. Even if the minimum is affecting climate, it may be of minimal consequence.
“. . . [O]nly about 10 percent of climate variation is due to the sun,” notes Leon Golub, senior astrophysicist at the Harvard-Smithsonian Institute for Astrophysics. “That means 90 percent isn’t.”
Just as importantly, the solar minimum won’t last forever, so any climatic effects are temporary, as well. But when will solar activity turn around? The current minimum began in 2000 and has been particularly deep for the last two years. At the AMS Annual Meeting, Joseph Kunches of NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center attempts to pinpoint the arrival of the next solar maximum and ponders its potential effects in his presentation, “Solar Cycle Update—Will the New Cycle Please Start?” (Monday, 2:15–2:30 p.m., B303). And Matthew J. Niznik and W. F. Denig of the National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service introduce a new indicator, the Genesis Minimum Quiet Day Index, which analyzes sunspot activity and suggests that the current solar minimum is not anomalous. Their index and the larger topic of the influence of solar activity on Earth’s climate are explored in their poster, “Impacts of Extended Periods of Low Solar Activity on Climate” (Monday, 2:30–4:00 p.m., exhibit hall B2).
Harsh Cold Wave Slowly Retreating
Well, the big winter cold snap that has been gripping much of the United States since December is nearing its end. Temperatures in most places from the Plains to the East Coast have started to rebound and no renewed surges of Arctic air are on the horizon after a final weak front moves through the East Tuesday. But the damage is done in places from the Dakotas and Montana to Florida: burst pipes, roads that drifted shut, and wind chills lower than -50 in the North, and car crashes on icy roads, power outages, and record cold that has chilled the South.
Last Thursday, the wind chill in Bowbells, North Dakota hit 52° F below zero. That degree of cold “freezes your nostrils, your eyes water, and your chest burns from breathing — and that’s just going from the house to your vehicle,” said Jane Tetrault of Burke County. Her vehicle started, but the tires were frozen. “It was bump, bump, bump all the way to work with the flat spots on my tires,” she said, adding, “It was a pretty rough ride.”
Snow and icy winds whipped southward from the Midwest into Tennessee, Georgia, and Alabama late in the week, making travel a disaster in Memphis and Atlanta. Video of cars sliding off roads or into each other played every half hour on The Weather Channel into the weekend.
Even the Sunshine State had wintry precipitation with this unusual cold surge—something not seen in more than 30 years. The weekend into Monday was especially brutal by Florida standards. With temperatures in the 30s and low 40s, light rain enveloped the peninsula Friday night through Saturday. Sleet fell in spots from Jacksonville and Ocala southward through Orlando, Tampa, and Melbourne into Palm Beach. A few wet snowflakes mixed in here and there with snow reported by trained spotters as far south as Kendall, a southern suburb of Miami. In some places north of Tampa, enough sleet accumulated on cars and outdoor furniture to build little “sleet” men, complete with tiny hats and tree-twig arms, their photos rivaling those taken of snowmen built in Tampa on January 17, 1977. (View a of Florida sleet from a snow and ice slideshow on Tampa’s baynews9.com.)
Clearing led to record morning lows both Sunday and Monday that threatened harm to Florida’s $3 billion citrus industry. Temperatures bottomed out at 25° in Tampa, 29° in Orlando, and 31° in Ft. Myers. On Sunday, the temperature in Miami tied the 1970 record for the date with 35°, and a 36° low Monday morning broke the previous record for the date of 37° set in 1927. Despite the records, it has been the duration of the cold, especially in the South, that makes this cold snap memorable. Morning after morning since the previous weekend, photos of Florida strawberries encased in ice showed up on newscasts. Such protective measures against the frigid temperatures are expected for several more mornings in central Florida, even as the chill slowly moderates.
The cold was even long-lasting in the Midwest and Plains, as noted in TWC meteorologist Tim Ballisty’s article “It’s Cold But So What?” last week. He points out that Chicago hasn’t been above freezing since Christmas Day, at the time 11 straight days and counting. Cleveland had 10 consecutive days of snow, and that count continued right into the weekend.
Unlike the extensive heat waves of recent summers, this long and harsh cold snap resulted in relatively few new temperature records. At the Annual Meeting in Atlanta, Gerry Meehl of NCAR will explore the rising ratio of record high temperatures to record low temperatures, which is expected to markedly increase by the middle of the century with current projections of climate warming.